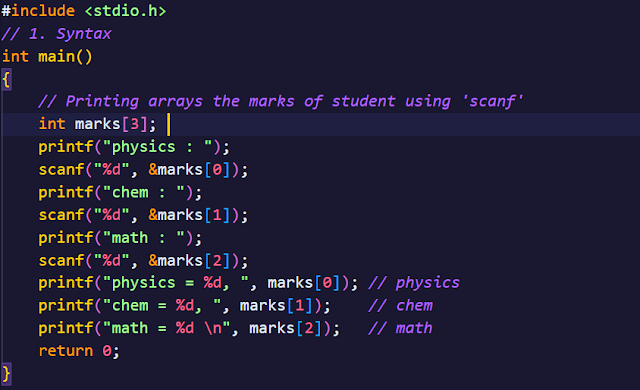
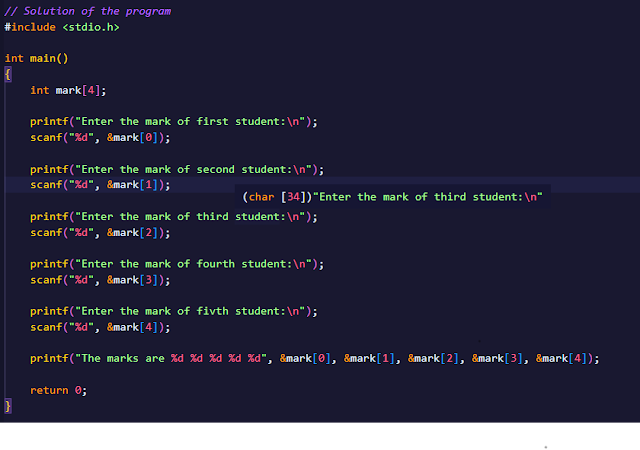
ARRAYS
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int m, n, sum = 0;
int a[3][4], b[4][2], result[3][2];
printf("Enter the First Matrix Elements \n");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i][j]);
}
}
printf("Enter the Second Matrix Elements \n");
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
scanf("%d", &b[i][j]);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
sum += a[i][k] * b[k][j];
}
result[i][j] = sum;
sum = 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
printf("%d \t", result[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
Memory Allocation
C is a language with some fixed rules of programming. For example: Changing the size of an array is not allowed.
DYNAMIC MEMORY ALLOCATION
Dynamic memory allocation is a way to allocate memory to a data structure during the runtime we can use DMA functions available in C to allocate and free memory during runtime.
FUNCTIONS FOR DMA IN C
Following Functions are available in C to perform Dynamic memory Allocation.
- malloc()
- calloc()
- free()
- realloc()
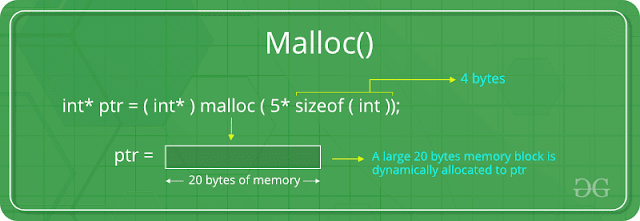
Malloc Function:
malloc stands for memory allocation. It takes a number of bytes to be allocated as input and returns a pointer of type void.
syntax:
NOTE: The expression returns a null pointer if the memory cannot be allocated.
PROGRAM:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main(){
//Declaring an integer pointer
int *ptr;
//storing malloc in ptr with 6 'int' variable
ptr = (int *)malloc(6*sizeof(int));
// Getting input from the user using for loop
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
printf("Enter the value of element %d \n",i);
scanf("%d", &ptr[i]);
}
// Printing user inputs using for loop
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
printf("The value of element %d is %d \n", i, ptr[i]);
}
OUTPUT:
Getting input from the user...
Enter the value of element 0
1
Enter the value of element 1
2
Enter the value of element 2
3
Enter the value of element 3
4
Enter the value of element 4
5
Enter the value of element 5
6
Printing the input value from the user...
The value of element 0 is 1
The value of element 1 is 2
The value of element 2 is 3
The value of element 3 is 4
The value of element 4 is 5
The value of element 5 is 6
Quick Quiz: Write a program to create a dynamic array of 5 floats using malloc().
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main(){
//Declaring a float variable
float *ptr;
// storing malloc in ptr
ptr = (float *)malloc(6*sizeof(float));
//Getting input from the user using for loop
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
printf("Enter the value of element %d \n",i);
scanf("%f", &ptr[i]);
}
//Printing input values using for loop
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
printf("The value of element %d is %f \n",i,ptr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Calloc() Function:
calloc stands for continuous allocation. it initializes each memory block with a default value of 0.
Syntax:
if the space is not sufficient memory allocation fails and a null pointer is returned.
Quick Quiz: Write a program to create an array of size n using calloc where n is an integer entered by the user.
// Declaring pointer variable
int *ptr;
int n;
//We used n here instead of a number
ptr = (int *)calloc(n, sizeof(int));
// Getting the size of n
printf("Enter a array size: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
//Getting input value using for loop
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("Enter the value of element %d \n",i);
scanf("%d", &ptr[i]);
}
// Printing input values using for loop
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("The value of element %d is %d \n",i,ptr[i]);
}












0 Comments